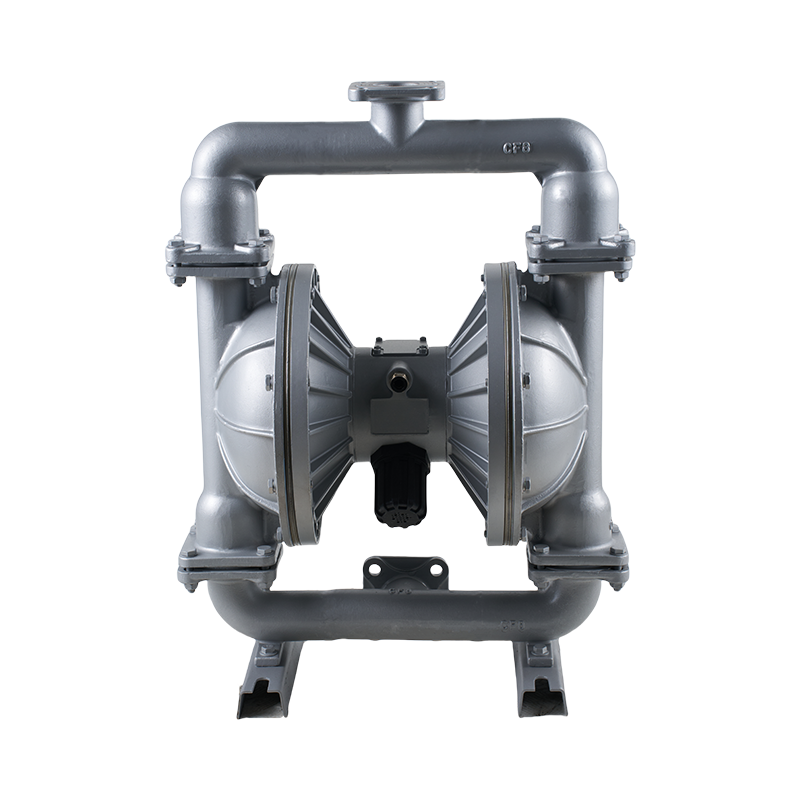
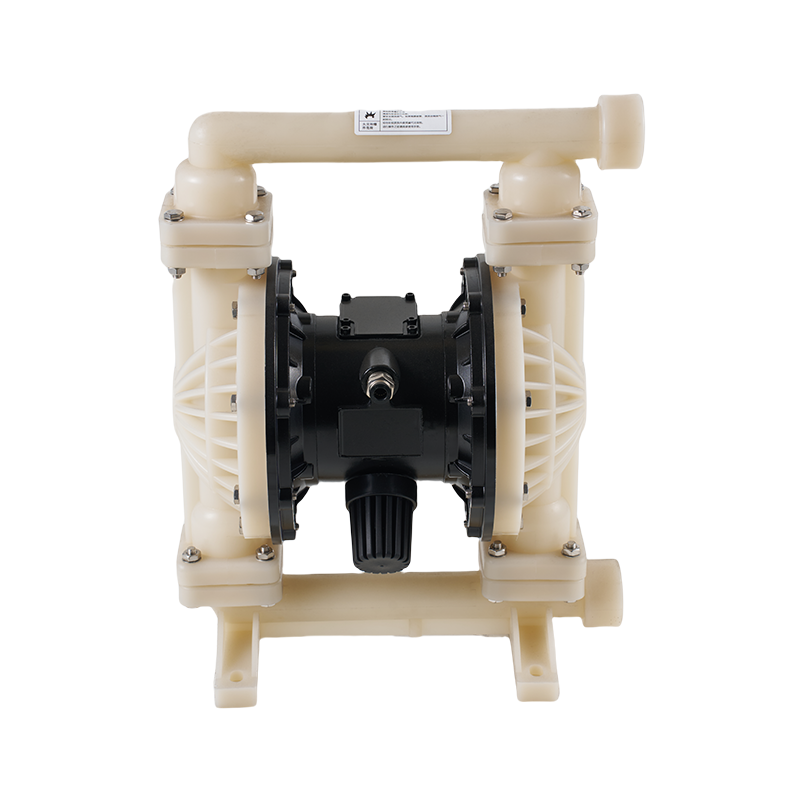
Advantages and Limitations of Diaphragm Pumps
 2025.09.19
2025.09.19
 Industry News
Industry News
Diaphragm pumps have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their versatility, reliability, and ability to handle a wide range of fluids. Many people are curious about the advantages of diaphragm pumps over other types of pumps, their potential limitations, and whether they are energy-efficient. This article explores these aspects in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of diaphragm pumps.
Advantages of Diaphragm Pumps
One of the main advantages of diaphragm pumps is their ability to handle a wide variety of fluids, including corrosive, abrasive, viscous, and even shear-sensitive liquids. Unlike centrifugal pumps, diaphragm pumps can manage fluids with high solid content without significant risk of clogging or damage. This makes them suitable for chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and food and beverage applications.
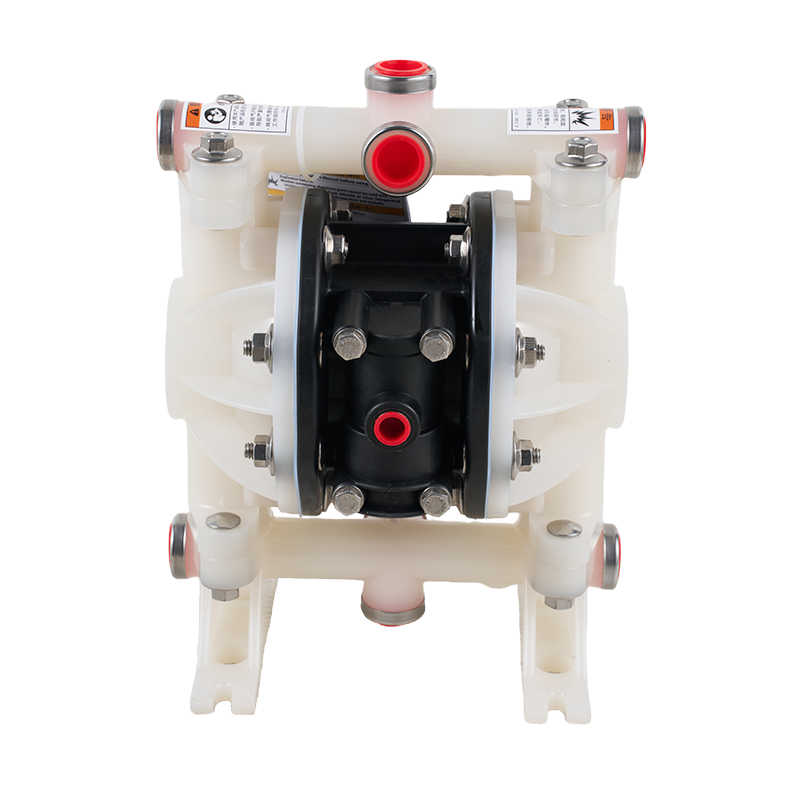
Another significant benefit of diaphragm pumps is their self-priming capability. They can start pumping even when the suction line is empty, which simplifies installation and operation. Additionally, many diaphragm pumps can run dry without causing damage, a feature that is particularly valuable in applications where flow interruption may occur.
Diaphragm pumps are also known for their leak-free operation. Since the pumped fluid is contained entirely within the diaphragm and valve system, there is minimal risk of fluid leakage. This characteristic is critical when handling hazardous chemicals or other sensitive liquids. The simple construction and limited moving parts contribute to low maintenance requirements, reducing downtime and operational costs compared to other pump types.
Limitations of Diaphragm Pumps
Despite their advantages, diaphragm pumps have some limitations that should be considered. One potential drawback is their lower flow rate compared to centrifugal pumps. While diaphragm pumps excel at handling challenging fluids and high-pressure applications, they may not be the choice for projects requiring very high volume flow.
Another limitation is the pulsating flow inherent in many diaphragm pumps. Unlike smooth-flow pumps such as gear or centrifugal pumps, diaphragm pumps produce a pulsating output that may require additional components, such as pulsation dampeners, to achieve consistent flow. For applications requiring extremely precise fluid delivery, this can be a factor to consider.
Diaphragm pumps may also experience wear over time, particularly in applications with abrasive materials. Although the diaphragm and valves are replaceable, frequent maintenance may be necessary in demanding conditions. Selecting the appropriate material for the diaphragm, such as PTFE or rubber, can mitigate wear and extend service life, but it may increase the initial cost.
Energy Efficiency of Diaphragm Pumps
When it comes to energy efficiency, diaphragm pumps generally perform well in specific scenarios but may not match the efficiency of some centrifugal pumps in high-flow, low-pressure applications. Air-operated diaphragm pumps, for example, rely on compressed air, which can be less energy-efficient than electrically driven pumps under continuous operation. On the other hand, mechanically driven diaphragm pumps tend to be more energy-efficient, particularly in applications requiring steady pressure and moderate flow rates.
Overall, the energy efficiency of a diaphragm pump depends on the type, driving mechanism, and application requirements. Proper pump selection and maintenance can help optimize energy use and reduce operational costs.
Diaphragm pumps offer numerous advantages, including the ability to handle diverse fluids, self-priming capabilities, leak-free operation, and low maintenance requirements. However, they have limitations, such as pulsating flow, lower flow rates, and potential wear when pumping abrasive materials. Their energy efficiency varies depending on the type of diaphragm pump and the application, with mechanically driven models generally being more efficient than air-operated versions. Understanding these advantages, limitations, and energy considerations allows users to make informed decisions and choose the right diaphragm pump for their specific needs.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى